24 Modal Aauxiliary Verbs List and Example Sentences

24 Modal Aauxiliary Verbs List and Example Sentences
Table of Contents
Modal Auxiliaries
What Are Modal Auxiliaries?
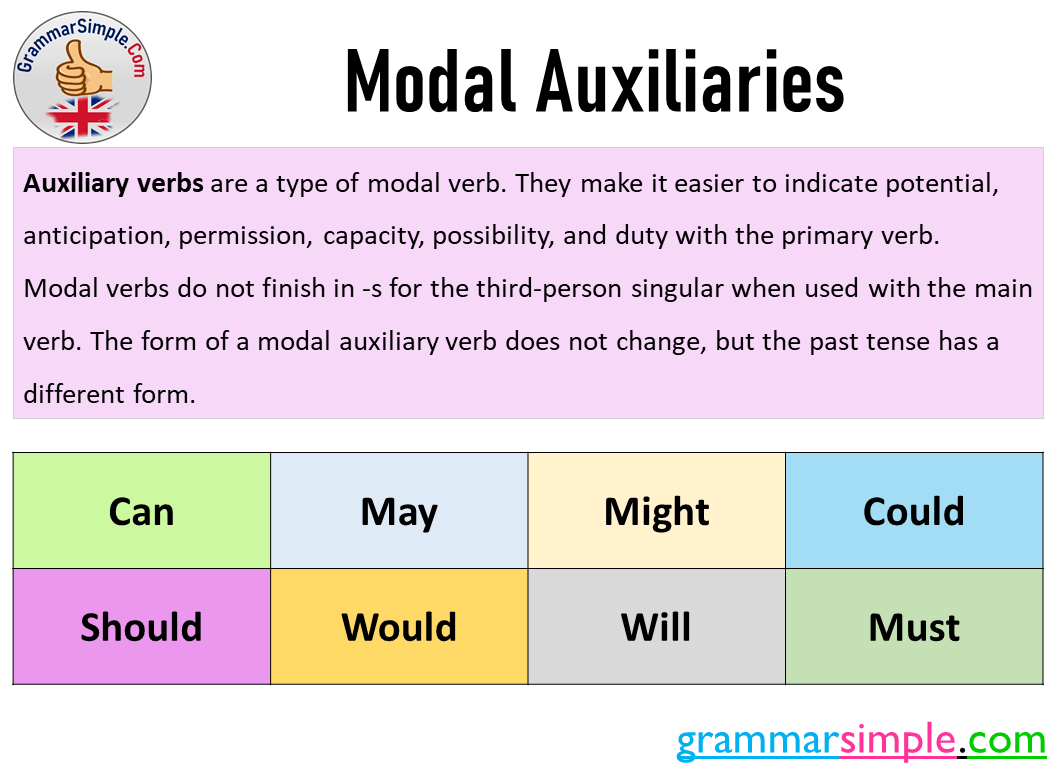
Auxiliary verbs are a type of modal verb. They make it easier to indicate potential, anticipation, permission, capacity, possibility, and duty with the primary verb.
Modal verbs do not finish in -s for the third-person singular when used with the main verb. The form of a modal auxiliary verb does not change, but the past tense has a different form.
| Present Tense | Past Tense |
| Will | Would |
| Can | Could |
| Must (have to) | (Had to) |
| May | Might |
| Should (ought to) (had better) | Should (ought to) |
Will – Would
The word “will” denote a desire to do something in the future. The negative version of “will – will not (won’t)” denotes a lack of willingness to accomplish something (refusal, reluctance).
- I will give you another chance.
- I will play with you tomorrow.
- They will arrive at 9 AM.
- She won’t come to the class today.
“Would” denotes prior broad or recurring willingness. It also expresses a current preference.
- If you did not give up, I would be proud of you so much.
- Whenever I had to go anywhere with her, she would send photos to her ex.
- We thought that people would buy this phone.
- If I were you, I would not do this.
Can – Could – May – Might
These modals convey the concepts of possibility and capacity.
The word “can” denotes capability. “Could” denotes a capability with a choice.
- He can do it. (The subject ‘He’ is sure about his ability)
- He could do it. (The subject ‘He’ is not sure about his ability)
- We cannot do it. (present)
- We could not do it. (past)
“Can & could” also indicate possibility.
- The temperature can get low this month.
- She can’t go too far by now.
- It could snow later.
“May” and “might” both convey the potential of something, but “might” can imply that it is less likely than “may.”
- It may snow later.
- It might snow later.
- She may come back tomorrow.
- She might come back tomorrow.
Must
“Must” indicates necessity.
- We must leave to catch the bus now.
- He must study hard for his finals.
- Ally must go home by 7.00 pm.
“Have to” is comparable to “must,” but it conveys a lower level of urgency.
- I have to leave right now.
- He has to study hard for his finals.
- Ally has to go by 7.00 pm.
- I had to leave then. (past)
- He had to study hard to pass his finals. (past)
Should
“Should” indicates obligation and probability.
- You should come home early today.
- You should not smoke in the classroom.
- We should visit my parents more often than usual.
- There should be an extra key for the lock. (probability)
- She should have reached. (probability)
- I should have done that to her mother. (Obligation in the past)
“Should” is occasionally replaced by “ought to” and “had better.”
- You ought to come home early today.
- We ought to have taken a car. (Past)
- We had better leave for now. (Had better is generally used in spoken English.)
Recent Posts
Use Rose in a Sentence, How to Use Rose with Example Sentences
Use Rose in a Sentence, How to Use Rose with Example Sentences
Use Yourself in a Sentence, How to Use Yourself with Example Sentences
Use Yourself in a Sentence, How to Use Yourself with Example Sentences
Use Picture in a Sentence, How to Use Picture with Example Sentences
Use Picture in a Sentence, How to Use Picture with Example Sentences
Use Claim in a Sentence, How to Use Claim with Example Sentences
Use Claim in a Sentence, How to Use Claim with Example Sentences
Use Treasure in a Sentence, How to Use Treasure with Example Sentences
Use Treasure in a Sentence, How to Use Treasure with Example Sentences
Use Raise in a Sentence, How to Use Raise with Example Sentences
Use Raise in a Sentence, How to Use Raise with Example Sentences